Transport accounts for about a quarter of Europe’s greenhouse gas emissions, with road traffic as a major source. Switching to electric DC railways and metro systems reduce emissions and save energy, but much of the braking energy goes unused, up to 1 GWh yearly per commuter line. Reversible DC substations (RSS) with power converters and storage can recover this energy. However, uncertainty about their actual energy benefits has slowed their adoption. Accurate measurement methods are needed to evaluate RSS performance in practice.
The European Partnership on Metrology project Metrology support for enhanced energy efficiency in DC transportation systems (e-Treny) addresses this by developing a traceable measurement infrastructure to monitor energy losses in metro and tramway conversion systems during regular operation. Innovative power measurement will now enable, for the first time, accurate assessment of losses in high-efficiency (> 97 %) converters within actual grid environments. These advances will provide valuable feedback to the transport sector and support future updates to European standards.
In 2024 and 2025, two major measurement campaigns were conducted: one on a 1500 V metro line in Madrid using a reversible substation, and another on a 700 V tramway line in Hannover featuring an on-ground storage system. The Madrid campaign successfully monitored energy flow in all the five substations supplying the line to support the optimization of energy efficiency and usage in urban rail networks.
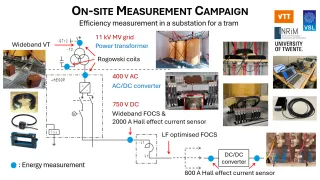
During the Hannover campaign carried out in May and June 2025, VTT, VSL, University of Twente, and INRIM, in close collaboration with Üstra and Alstom focused on monitoring the efficiency and power quality of key elements of a non-conventional, bi-directional tram substation: AC/AC power transformer, AC/DC power converter, and charge-discharge DC electric energy storage system. VTT coordinated the measurement setup design and the measurement system installation.
To guarantee reliable and accurate data, reference standards such as wideband voltage transformers, Rogowski coils, fibre optic current sensors, Hall effect current sensors, and power analysers were meticulously calibrated at National Metrology Institutes. These instruments were then deployed on-site, ensuring precise assessment of the overall substation power efficiency, as well as a closer look at the performance of each component.
Preliminary analysis is promising; in most scenarios, the substation system’s efficiency aligns with its design targets. Currently, the project is performing an even deeper dive — analysing efficiency across a variety of operational conditions and power levels, during both charging and discharging phases, and investigating the uncertainties involved in efficiency measurements.
These efforts of the e-Treny project mark a significant step towards more reliable and accurate metrological solutions for urban rail systems. By building trust in the reliability of RSS technology, e-Treny aims to accelerate its adoption, enhance public transport energy efficiency, and contribute to Europe’s climate goals. polishing, additive processes, and production optimisation to maintain consistent quality.